What Is Nucleophilic Addition Reaction With Example
Syn vs Anti In the last post on alkene addition reactions we discussed one of the two key themes to look for in addition reactions. 12-addition to the carbonyl function or 14-conjugate addition to the enone.
 Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
In this type of reaction a nucleophile such as an alcohol amine or enolate displaces the leaving group of an acyl derivative such as an acid halide anhydride or esterThe resulting product is a carbonyl-containing compound in which the nucleophile has taken the.

What is nucleophilic addition reaction with example. The mechanism for the addition of HCN to ethanal. A nucleophilic substitution is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species known as a nucleophile replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule known as the electrophileThe molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. Commonly a base such as NaOH or KOH is added to the aldehyde.
Simple alkyllithium reagents usually add in the 12-fashion but the presence of cuprous salts or the use of Gilmans reagent directs addition in the 14-fashion examples 20 21. Regiochemistry in other words what is the favored direction in which the pi-bond breaks. As before the reaction starts with a nucleophilic attack by the cyanide ion on the slightly positive carbon atom.
Nucleophilic addition reactions to αβ-unsaturated ketones may take place in two ways. Nucleophilic acyl substitution describe a class of substitution reactions involving nucleophiles and acyl compounds. It is completed by the addition of a hydrogen ion from for example a hydrogen cyanide molecule.
The reaction involves an aldehyde enolate reacting with another molecule of the aldehyde. The Aldol Reaction of Aldehydes Reaction type. Stereoselectivity In Alkene Addition Reactions.
This post is about the second key theme in addition reactions of alkenes. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following. Remember enolates are good nucleophiles and carbonyl C are good electrophiles.
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Nucleophilic Addition Reaction
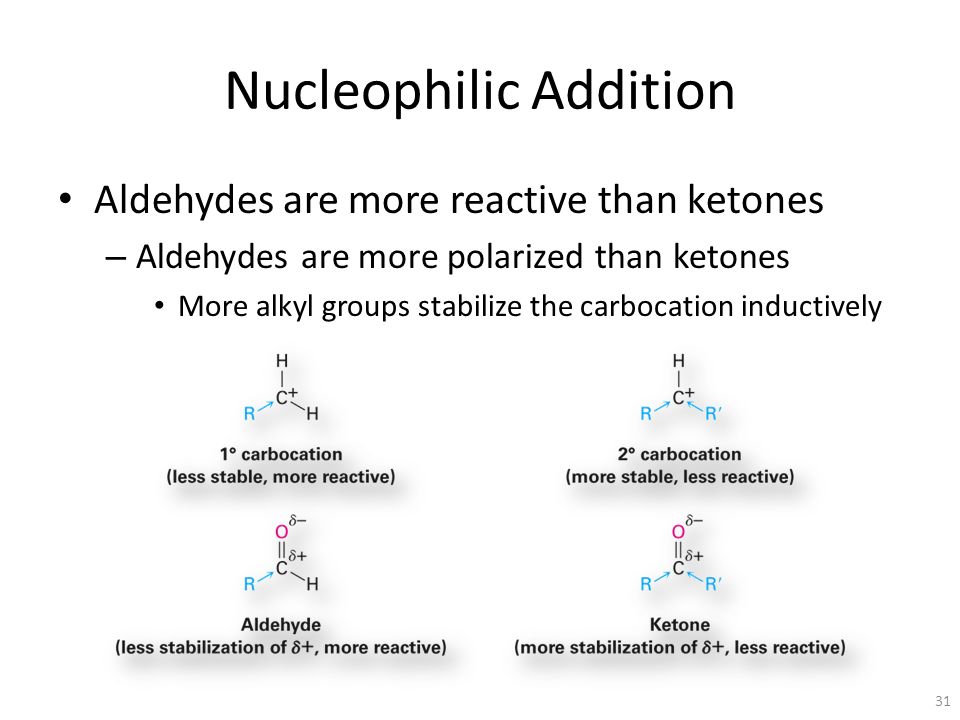 Chapter 19 Aldehydes And Ketones Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Ppt Video Online Download
Chapter 19 Aldehydes And Ketones Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Ppt Video Online Download
 Reactions Of Aldehydes And Ketones
Reactions Of Aldehydes And Ketones
 20 1 Introduction To Polar Pi Bonds Organic Chemistry Ii
20 1 Introduction To Polar Pi Bonds Organic Chemistry Ii
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions In Aldehydes And Ketones
 Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
 Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
What Is The Difference Between An Electrophilic Addition And A Nucleophilic Addition Is There A Rule Or Easy To Understand Pattern That Can Be Used To Differentiate Between The Two Types
Difference Between Addition And Substitution Reactions Definition Types Characteristics Examples Comparison
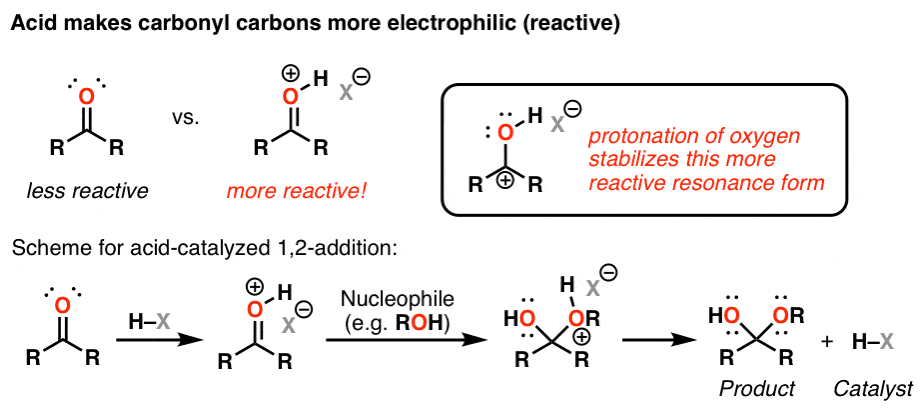 Acid Catalysis With Nucleophiles The Goldilocks Point
Acid Catalysis With Nucleophiles The Goldilocks Point
 Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Aldehydes And Ketones I Electrophilicity And Oxidation Reduction Mcat Organic Chemistry Review
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Aldehydes And Ketones I Electrophilicity And Oxidation Reduction Mcat Organic Chemistry Review
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Nucleophilic Addition Reaction
 Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism
Addition Reaction Definition Examples And Mechanism
 Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction General Mechanism Examples
 Nucleophilic Addition Reaction Types Mechanism Examples And Videos
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction Types Mechanism Examples And Videos
Write Mechanism Of Nucleophilic Addition Reaction By Taking A Suitable Example Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
 Nucleophilic Addition Reaction Mechanism Grignard Reagent Nabh4 Lialh4 Imine Enamine Reduction Youtube
Nucleophilic Addition Reaction Mechanism Grignard Reagent Nabh4 Lialh4 Imine Enamine Reduction Youtube